
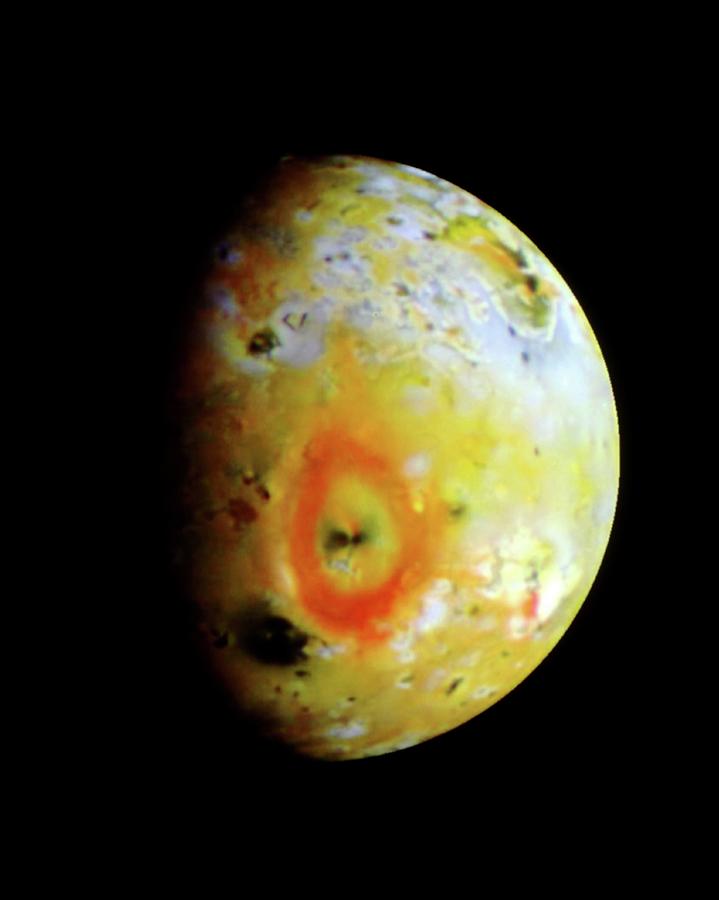
But, Pioneer 11 was able to verify that the polar region had an orange color, contrasting with the whitish equator. Pioneer 10 was not able to obtain any clues regarding the radiation of Io. With the passage of the space probe, Pioneer in the 1970s, little was discovered about Io. In the middle of the 20th Century observations were made suggesting that the polar regions of Io were red. Galileo doubted this claim and catalogued the work of Marius as plagiarism. In his Mundus Jovialis, published in 1614, Simon Marius claimed to have discovered Io and the other moons of Jupiter in 1609, one week before Galileo's discovery. The moon Io is believed to have been discovered on 7 January, 1610 by Galileo. 1 History of observation and exploration.In much of the earlier astronomical literature, Io is simply referred to by its Roman numeral designation as " Jupiter I", or simply as "the first satellite of Jupiter". It is named after the Greek mythological figure Io, one of the many lovers of Zeus (who is also known as Jupiter in the Roman mythology).Īlthough the name "Io" was suggested by Simon Marius soon after its discovery in 1610, this name and the names of the other Galilean satellites fell into disfavor for a considerable time, and were not revived in common use until the mid-20th century. Io shines at magnitude 5.0 in the night sky.

Io (eye'-oe, ˈaɪoʊ, Greek Ῑώ) is the innermost of the four Galilean moons of Jupiter.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
